Oral spray vs. tablets
Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile Dysfunction or Male Sexual Impotence is defined as the persistent inability (over three months or more) to obtain and maintain an erection that allows satisfactory sexual intercourse. It is a problem that affects males and can occur at any age, although it is more common in older age groups.
Erectile dysfunction affects 29% of men between the ages of 40 and 49, 50% between 50 and 59 and 74% between 60 and 69. It is estimated that in Portugal it affects around 500,000 men
Despite being a benign disease, sexual impotence has a major impact on a man’s sex life as well as on a psychological level. Given its influence on self-esteem, many men don’t seek help, which tends to make the problem worse. However, the majority of cases are treatable, around 90%.
Warning signs
In addition to the difficulty in getting or maintaining an erection, erectile dysfunction can manifest itself in various ways.
- decreased sex drive
- Changes in erection quality
- Difficulty in penetration
- Ejaculatory changes
- Difficulty ejaculating
Causes
Erectile dysfunction can have various causes, including:
- Health problems: heart disease, diabetes, hypertension, atherosclerosis, spinal cord injuries, among others
- Lifestyle: excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, sedentary lifestyle
- Psychological factors: anxiety, stress, depression, low self-esteem
- Relationship problems: communication problems with partner, lack of intimacy
- Use of medication: some drugs can affect erectile function, such as those used to treat hypertension and depression.
These are just some of the possible causes of erectile dysfunction. It is important to consult a urologist to determine the exact cause and define the appropriate treatment.
Treatment
Although there are many options for treating erectile dysfunction today, therapy should not be started without a doctor’s prescription. It is the clinician who defines the treatment, personalizing it according to the causes and degree of severity of the erectile dysfunction. Treatment can be divided into three categories – non-pharmacological (psychological or psychiatric support), pharmacological (with the prescription of drugs that promote blood supply to the penis) and other approaches, including surgery.
An oral suspension (oral spray) that promotes erection. This oral spray allows for flexible doses, with a greater or lesser number of sprays (each spray provides 12.5 mg). It works by relaxing the blood vessels in the penis, allowing blood to flow to it when sexually stimulated.
There are currently four oral drugs in the class of phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors. These drugs promote erection by relaxing the blood vessels in the penis, allowing blood to flow to it when sexually stimulated.
For men with moderate erectile dysfunction who are contraindicated or have not responded to treatment with oral medication, self-administered injections of prostaglandins can be offered, which are applied to the penis before sexual intercourse. There are other options, such as topical prostaglandins, which are applied locally to the male urethra and have a vasodilatory effect.
There is also the possibility of having a penile prosthesis fitted, which is a third-line treatment for erectile dysfunction. This intervention is reserved for men who have not responded to previous treatments or who are looking for a longer-lasting solution. Vascular surgery – another possible treatment for erectile dysfunction – aims to increase arterial flow and decrease venous return.
This strategy, which includes the support of a psychotherapist or psychiatrist, will be recommended in cases where erectile dysfunction is associated with stress, anxiety or depression. The non-pharmacological approach can complement other forms of treatment for Erectile Dysfunction. Before instituting a drug strategy, a change in lifestyle should be tried, involving, for example, quitting smoking and drinking alcohol, as well as promoting physical exercise and a healthy diet.
 Oral Suspension
Oral Suspension
Innovative drug for the treatment of erectile dysfunction in the form of an oral spray.
This presentation in the form of an oral spray allows for flexible doses, with a greater or lesser number of sprays.
Advantages
- Allows for flexible doses
- Ensures the right doses for each spray
- Does not need to be taken with water
- Practical
Acting
This medicine works by relaxing the blood vessels in the penis, allowing blood to flow to the penis when sexually stimulated.
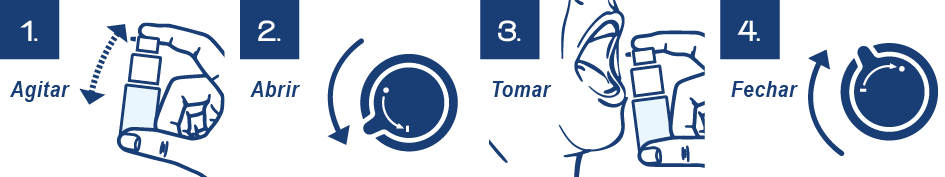
Mode of administration
Access the detailed instructions for use here
Drug absorption via the oral mucosa
The oral mucosa has a thin epithelium and abundant blood vessels, which promote rapid absorption of the drug into the bloodstream. As the oral mucosa is highly vascularized, drugs absorbed through this mucosa enter the bloodstream directly, resulting in a faster onset of action than drugs administered by the traditional oral route.
 Tablets
Tablets
There are currently four oral drugs in the class of phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors.
Acting
This medicine works by relaxing the blood vessels in the penis, allowing blood to flow to the penis when sexually stimulated.
Disadvantages
- Needs to be taken with water
- Splitting the tablets can lead to inaccurate doses and improper storage of the remainder
Editorial Note: This page and all other contents present in
lifewell.pt
are prepared and reviewed by medical experts in Portugal.